

The subjects in the group with RI are divided into 4 stages according to GFR rate: first stage (60-89.99ml / min / 1.73m2) (25%), second stage (30 to 59.99 ml / min / 1.73m2) 40%, third stage (15 to 29.99 ml / min / 1.73m2) and 20% of the fourth stage (≤14, 99 ml / min / 1.73m2) 15% of the subjects. The survey was conducted on 562 subjects divided into two groups with and without renal insufficiency. Apart from the mentioned facts, anemia in kidney patients is not recognized and treated at the right time therefore this study has an aim to establish a quantitative relationship between the concentration of erythropoietin, hemoglobin and hematocrit in different values, glomerular filtration rate, and to determine the legality of these connections. The treatment for anemia with recombinant erythropoietin should be initiated on the basis of glomerular filtration rate and hemoglobin, but it is not enough clarified yet ( 7, 8). In studies of patients with chronic kidney disease a direct correlation degree of anemia (concentration of Hb) and renal failure ( 6) has been demonstrated. With the fall of the value of glomerular filtration rate the incidence of anemia is increased. Renal anemia is a consequence of chronic kidney disease and occurs at an early stage, it gets worse as the disease progresses ( 4, 5). Large amount of studies that were conducted show that every tenth person in the world has a chronic kidney disease.
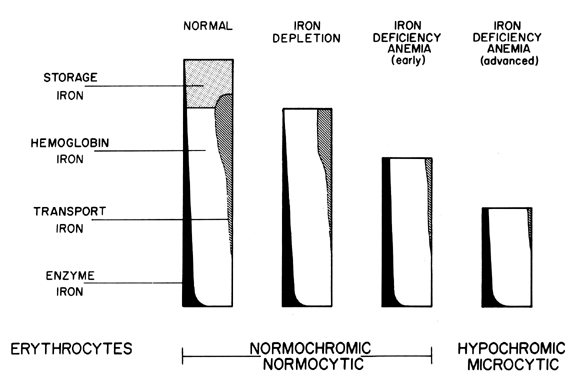

Anemia is an independent risk factor for development of cardiovascular diseases in patients with chronic kidney disease. For the normal maturation of erythrocytes, except erythropoietin, it is essential to have iron, folic acid and vitamin B12. The most important reason of anemia is the inability of the kidneys to increase the synthesis of EPO in response to it ( 4, 8). Anemia is diagnosed by measuring hemoglobin (Hb) levels (g / L) and hematocrit (Hct) (percentage of red blood cells in the blood) and by comparison with a given reference values. Anemia is one of the most common disorders in chronic renal insufficiency ( 3- 7). The level of synthesis of EPO in the kidneys (or liver) is primarily governed by the needs of the given cells for oxygen. EPO stimulates the proliferation and differentiation of erythroid precursor cells in the bone marrow and in this way it affects the production of red cells ( 1, 2).Ĭhronic renal insufficiency leads to hypo-regenerative anemia due to the lack of erythropoietin. With further deterioration of renal function the values of EPO between all pathological groups are decreasing, and this decrease is statistically significant between first and second degree of renal insufficiency (RI) p0.05.Įrythropoietin is a glycoprotein hormone composed of 165 amino acid residues with four complex carbohydrate chains attached with peptide in the four binding positions (MW 30.4 kDa), and it has the role of the primary regulator of erythropoiesis. EPO values (median) grow to the first degree of renal insufficiency, as compared to EPO values of healthy subjects, this increase is statistically significant, p=0.002.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
